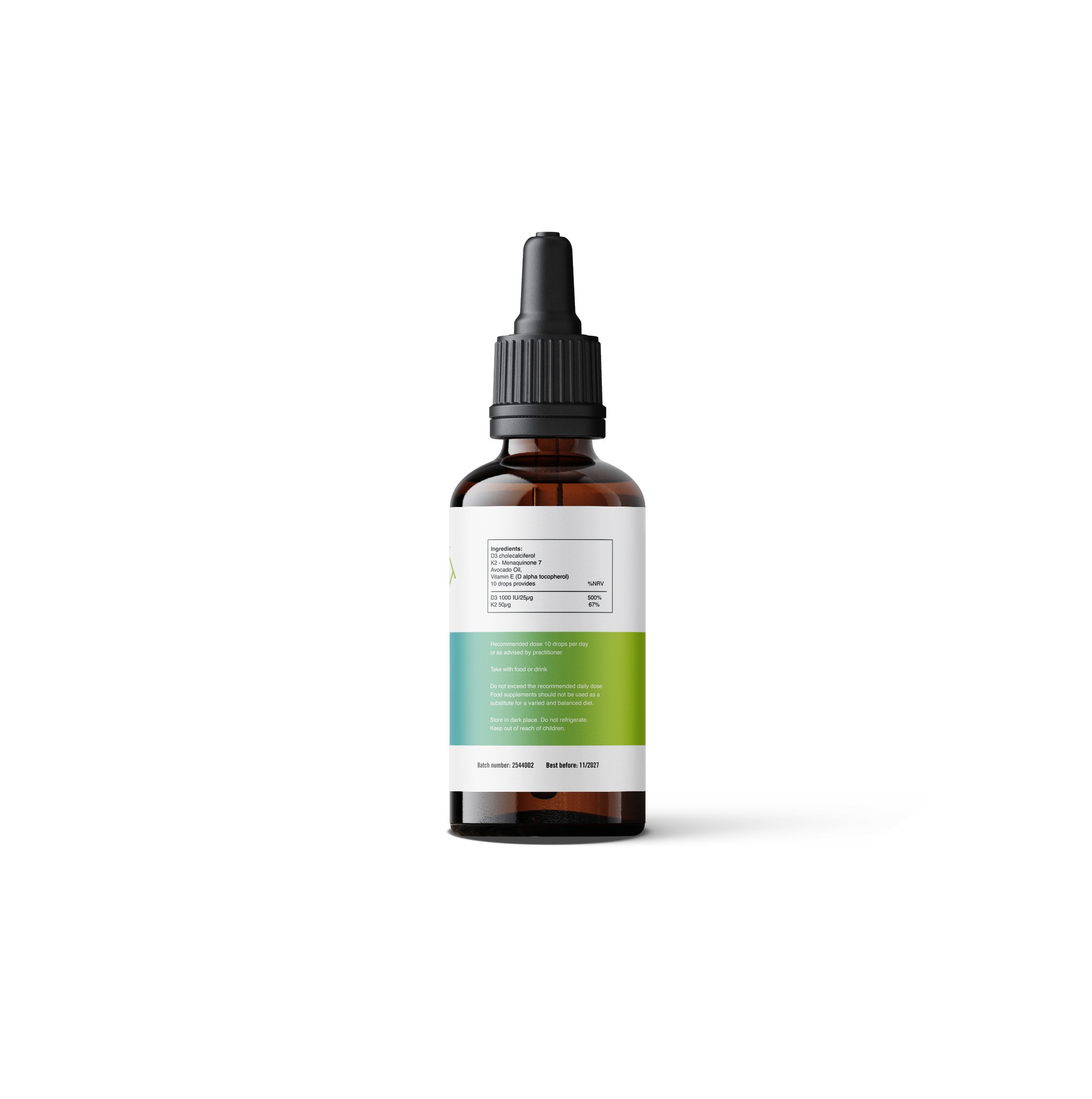
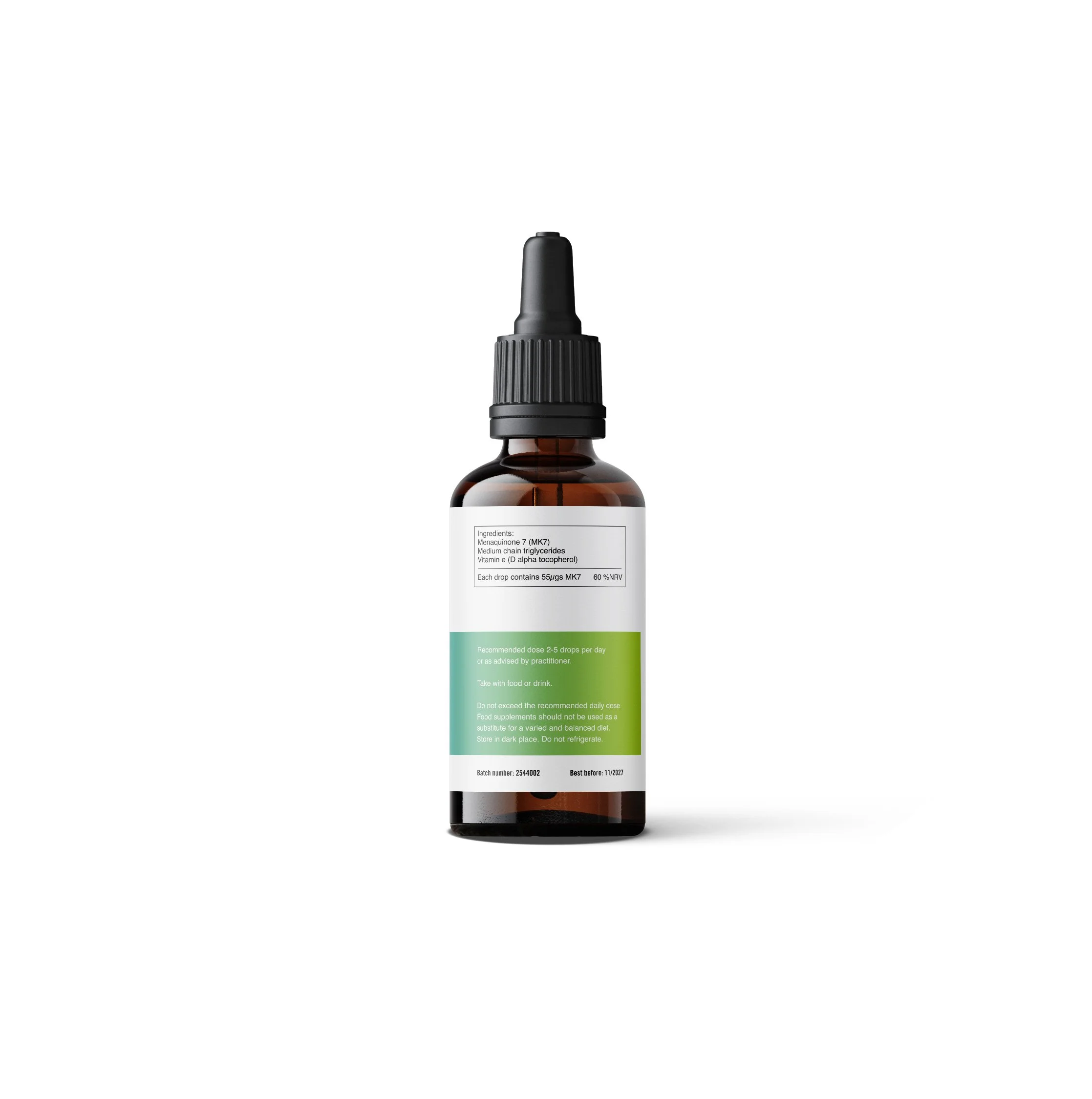
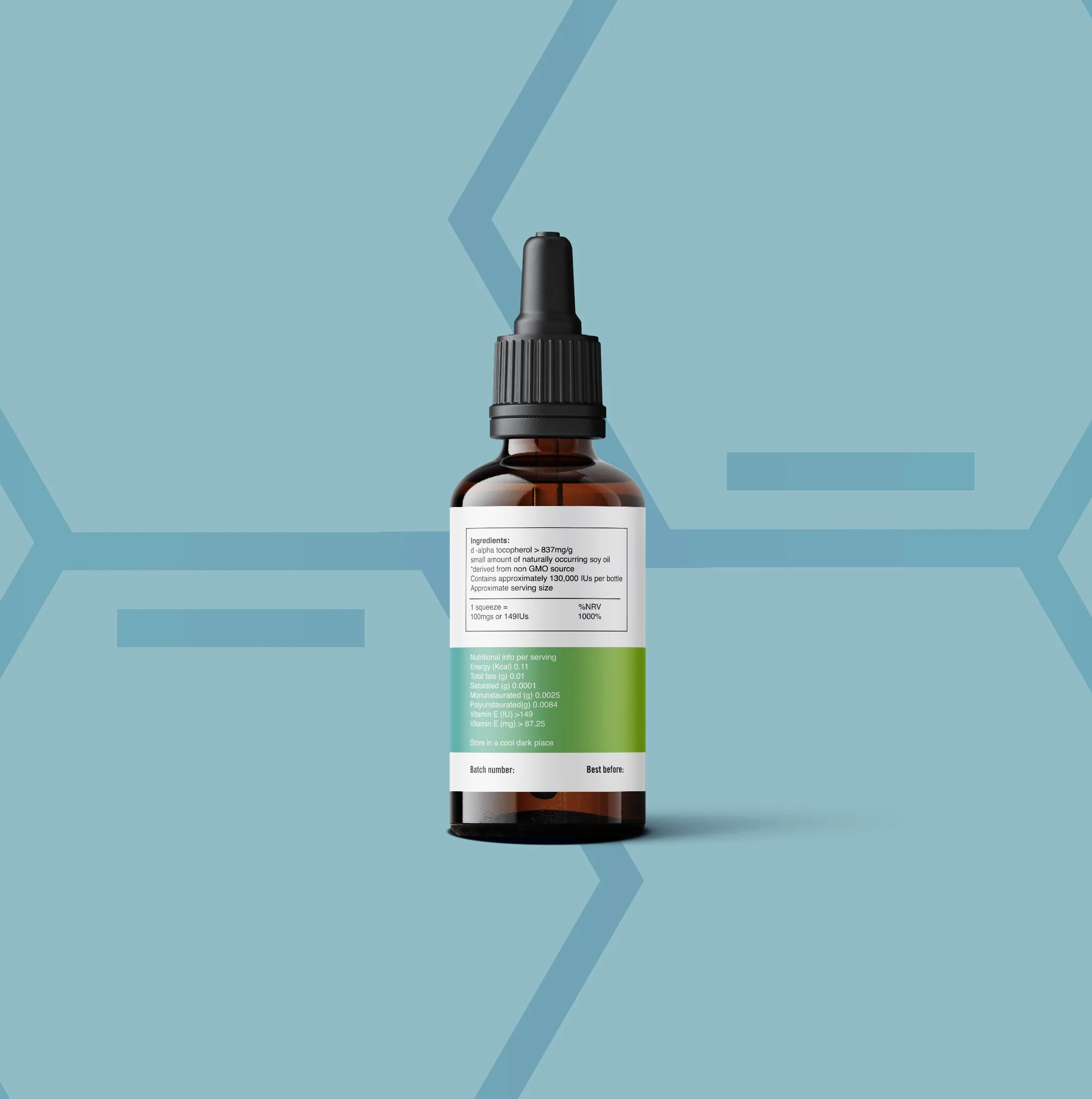
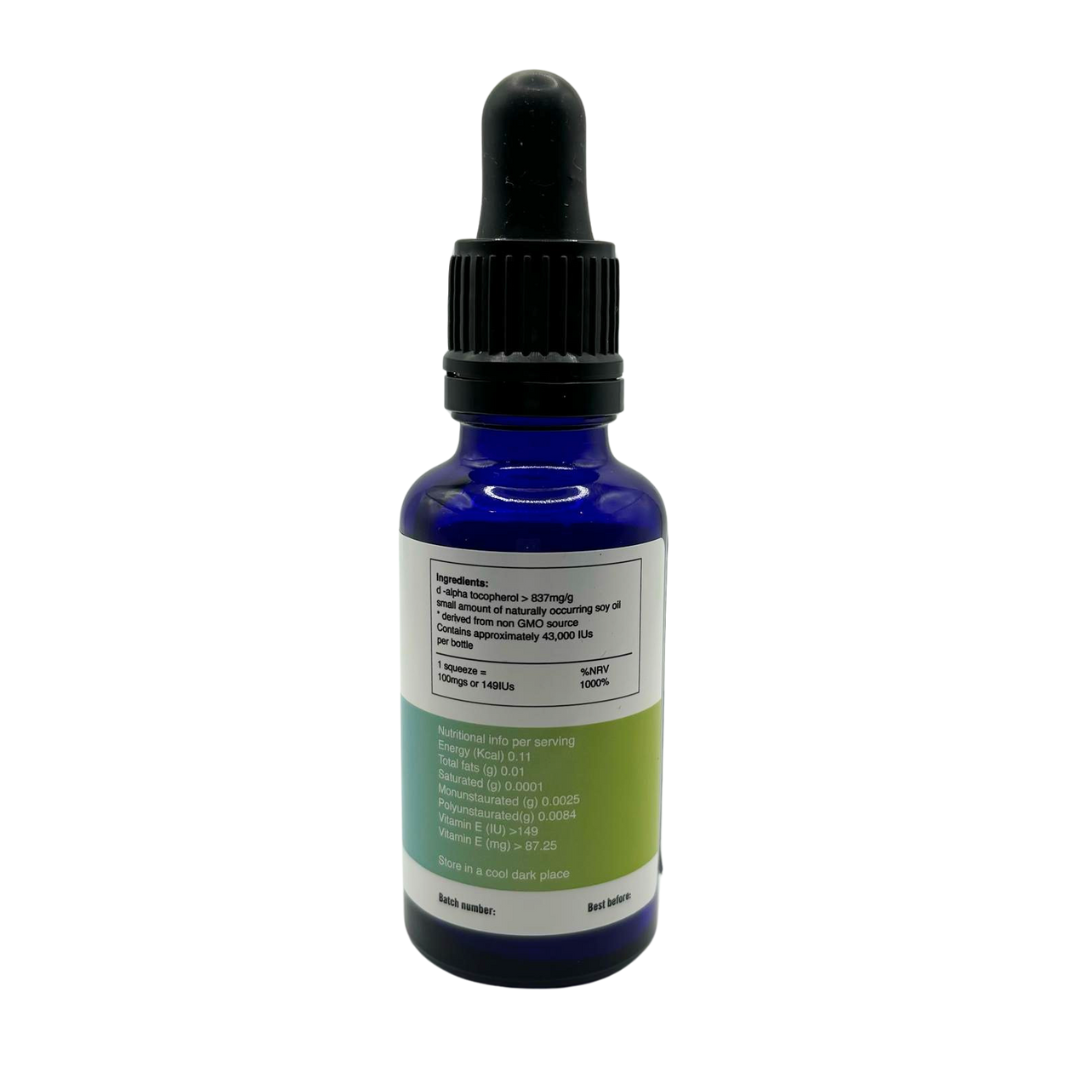
Hesperidin is a flavanoid contained in citrus fruits and has shown useful properties for decreasing histamine responses, improving motion sickness, acts as an antimicrobial agent and cardiovascular protection. (60 capsules)
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15240993/
The inhibitory activity of hesperetin was found to be comparable with azelastine, a commercially available antiallergic drug, and to potently inhibit prostaglandin E2 production in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Hesperetin weakly inhibits cyclooxygenase 2 enzyme activities. These results suggest that hesperidin may be a prodrug, which is metabolized to hesperetin by intestinal bacteria.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25625242/
The results of the recent basic and clinical studies revealed the beneficial effects for Hst, Hsd and their derivatives in the treatment of heart failure and cardiac remodeling, myocardial ischemia and infarction, and hypertension. In addition, the valuable effects of Hst and Hsd in the treatment of diabetes and dyslipidemia with their anti-platelet and anticoagulant effects make them good candidates in the treatment of various cardiovascular diseases. In this review, new findings regarding the molecular targets of Hsd and Hst, animal studies and clinical trials are discussed.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31782104/
"Pre-treatment with HSP inhibited histamine, HRH1 mRNA and protein expression. Histamine, HRH1 mRNA and protein expression in hypothalamus and brainstem samples of MS group increased significantly when compared to the NC group. Pre-treatment with HSP significantly reduced histamine, HRH1 mRNA and protein expression. Thus, indicating that HSP has a potent anti- MS effect by decreasing the elevated levels of histamine, HRH1 mRNA and protein expression in hypothalamus and brainstem regions."
Hesperidin is a flavanoid contained in citrus fruits and has shown useful properties for decreasing histamine responses, improving motion sickness, acts as an antimicrobial agent and cardiovascular protection. (60 capsules)
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15240993/
The inhibitory activity of hesperetin was found to be comparable with azelastine, a commercially available antiallergic drug, and to potently inhibit prostaglandin E2 production in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Hesperetin weakly inhibits cyclooxygenase 2 enzyme activities. These results suggest that hesperidin may be a prodrug, which is metabolized to hesperetin by intestinal bacteria.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25625242/
The results of the recent basic and clinical studies revealed the beneficial effects for Hst, Hsd and their derivatives in the treatment of heart failure and cardiac remodeling, myocardial ischemia and infarction, and hypertension. In addition, the valuable effects of Hst and Hsd in the treatment of diabetes and dyslipidemia with their anti-platelet and anticoagulant effects make them good candidates in the treatment of various cardiovascular diseases. In this review, new findings regarding the molecular targets of Hsd and Hst, animal studies and clinical trials are discussed.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31782104/
"Pre-treatment with HSP inhibited histamine, HRH1 mRNA and protein expression. Histamine, HRH1 mRNA and protein expression in hypothalamus and brainstem samples of MS group increased significantly when compared to the NC group. Pre-treatment with HSP significantly reduced histamine, HRH1 mRNA and protein expression. Thus, indicating that HSP has a potent anti- MS effect by decreasing the elevated levels of histamine, HRH1 mRNA and protein expression in hypothalamus and brainstem regions."